Kidney Cancer Treatment in Purnea
What Is Kidney Cancer?
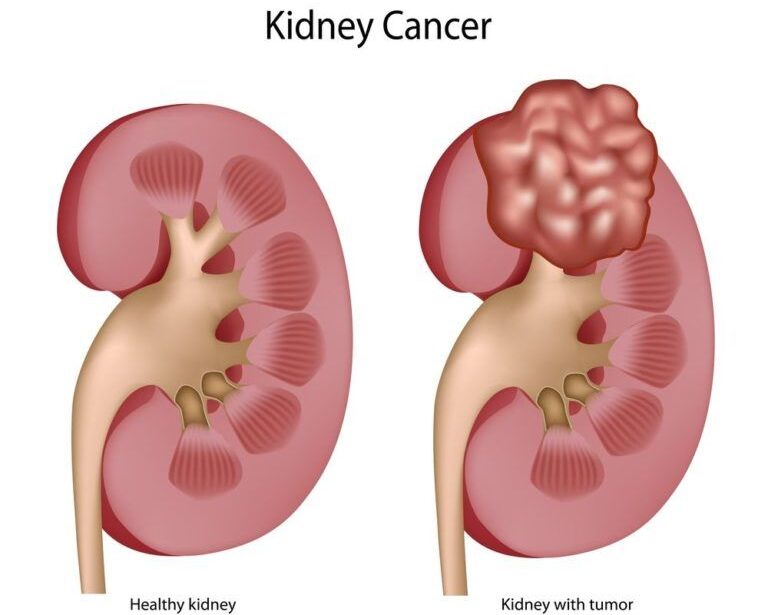
Kidney cancer — also called renal cancer — is a disease in which kidney cells become malignant (cancerous) and grow out of control, forming a tumor. Almost all kidney cancers first appear in the lining of tiny tubes (tubules) in the kidney. This type of kidney cancer is called renal cell carcinoma. The good news is that most kidney cancers are found before they spread (metastasize) to distant organs. And cancers caught early are easier to treat successfully. However, these tumors can grow to be quite large before they are detected.
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They lie in your abdomen on each side of your spine. Their main job is to clean your blood, removing waste products and making urine.
Doctors don’t know the causes of kidney cancer. But certain factors appear to increase the risk of getting kidney cancer. For example, kidney cancer occurs most often in people older than age 40. These are some other risk factors for kidney cancer:
- Smoking. If you smoke cigarettes, your risk for kidney cancer is twice that of nonsmokers. Smoking cigars may also increase your risk.
- Being male. Men are about twice as likely as women to get kidney cancer.
- Being obese. Extra weight may cause changes to hormones that increase your risk.
- Using certain pain medications for a long time. This includes over-the-counter drugs in addition to prescription drugs.
- Having advanced kidney disease or being on long-term dialysis, a treatment for people with kidneys that have stopped working
- Having certain genetic conditions, such as von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease or inherited papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Having a family history of kidney cancer. The risk is especially high in siblings.
- Being exposed to certain chemicals, such as asbestos, cadmium, benzene, organic solvents, or certain herbicides
- Having high blood pressure. Doctors don’t know whether high blood pressure or medication used to treat it is the source of the increased risk.
- Being Black. The risk in Blacks is slightly higher than in whites. No one knows why.
- Having lymphoma. For an unknown reason, there is an increased risk of kidney cancer in patients with lymphoma.
What Are the Symptoms of Kidney Cancer?
In many cases, people may have no early symptoms of kidney cancer. As the tumor grows larger, symptoms may appear. You may have one or more of these kidney cancer symptoms:
- Blood in your urine
- A lump in your side or abdomen
- A loss of appetite
- A pain in your side that doesn’t go away
- Weight loss that occurs for no known reason
- Fever that lasts for weeks and isn’t caused by a cold or other infection
- Extreme fatigue
- Anemia
- Swelling in your ankles or legs
Kidney cancer that spreads to other parts of your body may cause other symptoms, such as:
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
- Bone pain